A ratiometric photoacoustic imaging approach for semi-quantitative determination of aggregation efficiency in vivo†
Abstract
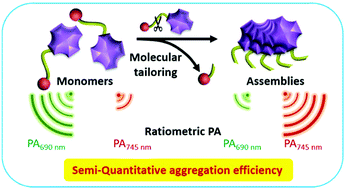
In vivo self-assembly not only endows dynamic supramolecules with various biological functions, but also realizes metabolic differences, and improves the level of diagnosis and treatment. However, the method of measuring aggregation efficiency in vivo is still challenging. In this work, we first proposed a ratiometric photoacoustic imaging method to measure the aggregation efficiency of molecules in vivo in real time and semi-quantitatively. Similar to the traditional fluorescence method, the ratiometric photoacoustic signal has a typical exponential relationship with the aggregation efficiency, which is defined as the percentage of aggregation molecules in the total molecules. Then, we proposed a ratiometric photoacoustic (PA) probe, which can be tailored by cathepsin E and self-assembled into nanofibers in situ inside pancreatic cancer cells. The maximum aggregation efficiency of 10−5 M PA probe was 58% after 2 hours of incubation. After intratumoral administration in xenografted pancreatic tumor mice, the highest aggregation efficiency was found to be 36% 6 hours after the injection. The ratiometric PA probe provides us with a real-time method to detect the aggregation efficiency in vivo, which is helpful to deepen the understanding of the dynamic assembly process and optimize the design of supramolecules.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Research selection from the NCNST

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...