AgPd nanoparticles for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction: bimetallic composition-dependent ligand and ensemble effects†
Abstract
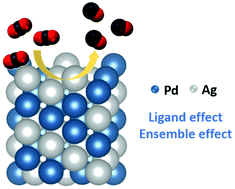
Monodisperse AgPd nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized and studied as an efficient catalyst for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction by modulating bimetallic compositions. The mechanistic studies, based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations and environmental diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) analysis, revealed that the incorporation of Ag in AgPd NPs can effectively weaken CO adsorption on all possible Pd surface sites (the ligand effects), and more importantly, disrupt the strongest multi-centered CO-binding sites (the ensemble effects). With properly tuned CO adsorption, which is ordinarily too strong over pure Pd, Ag15Pd85 NPs were found to be the best composition for the efficient production of CO. They deliver a unity conversion of CO2 to CO with a high mass activity of 15.2 mA mgmetal−1 at −0.8 V vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) and high stability with minimal change in the CO faradaic efficiency (FECO) after 12 hours of operation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...