Dissecting the intracellular signalling and fate of a DNA nanosensor by super-resolution and quantitative microscopy†
Abstract
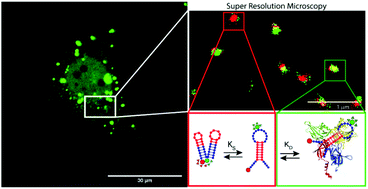
DNA nanodevices have been developed as platforms for the manipulation of gene expression, delivery of molecular payloads, and detection of various molecular targets within cells and in other complex biological settings. Despite efforts to translate DNA nanodevices from the test tube (in vitro) to living cells, their intracellular trafficking and functionality remain poorly understood. Herein, quantitative and super-resolution microscopy approaches were employed to track and visualise, with nanometric resolution, the molecular interactions between a synthetic DNA nanosensor and transcription factors in intracellular compartments. Specifically, fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and multicolour single-molecule localisation microscopy were employed to probe the specific binding of the DNA nanosensor to the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB). We monitored the mobility, subcellular localisation and degradation of the DNA nanosensor inside living prostate cancer PC3 cells. Super-resolution imaging enabled the direct visualisation of the molecular interactions between the synthetic DNA nanosensors and the NF-κB molecules in cells. This study represents a significant advance in the effective detection as well as understanding of the intracellular dynamics of DNA nanosensors in a complex biological milieu.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...