Multilayer electrodeposition of Pt onto 1–2 nm Au nanoparticles using a hydride-termination approach†
Abstract
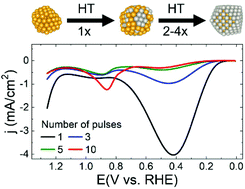
Here we report on hydride-terminated (HT) electrodeposition of Pt multilayers onto ∼1.6 nm Au nanoparticles (NPs). The results build on our earlier findings regarding electrodeposition of a single monolayer of Pt onto Au NPs and reports relating to HT Pt electrodeposition onto bulk Au. In the latter case, it was found that electrodeposition of Pt from a solution containing PtCl42− can be limited to a single monolayer of Pt atoms if it is immediately followed by adsorption of a monolayer of H atoms. The H-atom capping layer prevents deposition of Pt multilayers. In the present report we are interested in comparing the structure of NPs after multiple HT Pt electrodeposition cycles to the bulk analog. The results indicate that a greater number of HT Pt cycles are required to electrodeposit both a single Pt monolayer and Pt multilayers onto these Au NPs compared to bulk Au. Additionally, detailed structural analysis shows that there are fundamental differences in the structures of the AuPt materials depending on whether they are prepared on Au NPs or bulk Au. The resulting structures have a profound impact on formic acid oxidation electrocatalysis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
