Stable, concentrated, biocompatible, and defect-free graphene dispersions with positive charge†
Abstract
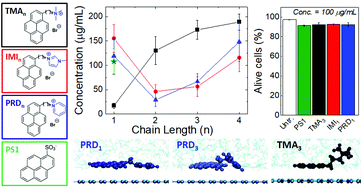
The outstanding properties of graphene offer high potential for biomedical applications. In this framework, positively charged nanomaterials show better interactions with the biological environment, hence there is strong interest in the production of positively charged graphene nanosheets. Currently, production of cationic graphene is either time consuming or producing dispersions with poor stability, which strongly limit their use in the biomedical field. In this study, we made a family of new cationic pyrenes, and have used them to successfully produce water-based, highly concentrated, stable, and defect-free graphene dispersions with positive charge. The use of different pyrene derivatives as well as molecular dynamics simulations allowed us to get insights on the nanoscale interactions required to achieve efficient exfoliation and stabilisation. The cationic graphene dispersions show outstanding biocompatibility and cellular uptake as well as exceptional colloidal stability in the biological medium, making this material extremely attractive for biomedical applications.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Celebrating our 2020 Prize and Award winners and Advisory Board research selection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...