3D bioprinting of cell-laden electroconductive MXene nanocomposite bioinks†
Abstract
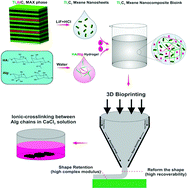
MXenes, a new family of burgeoning two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides/nitrides, have been extensively explored in recent years owing to their outstanding properties such as a large specific surface area, high electrical conductivity, low toxicity, and biodegradability. Numerous efforts have been devoted to exploring MXenes for various biomedical applications such as cancer therapy, bioimaging, biosensing, and drug delivery. However, the potential application of MXene nanosheets in tissue engineering has been almost overlooked despite their excellent performance in other biomedical applications. The overarching goal of this paper is to demonstrate the potential of MXene cell-laden bioinks for tissue engineering and their ability to assemble functional scaffolds to regenerate damaged tissue via 3D bioprinting. We formulate a new electroconductive cell-laden bioink composed of Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets dispersed homogeneously within hyaluronic acid/alginate (HA/Alg) hydrogels and showed its performance for extrusion-based 3D bioprinting. The prepared hydrogel bioinks with MXenes display excellent rheological properties, which allows the fabrication of multilayered 3D structures with high resolution and shape retention. Moreover, the introduction of Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets within the HA/Alg hydrogel introduces electrical conductivity to the ink, addressing the poor electrical conductivity of the current bioinks that mismatch with the physico-chemical properties of tissue. In addition, the MXene nanocomposite ink with encapsulated Human Embryonic Kidney 293 (HEK-293) cells displayed high cell viability (>95%) in both bulk hydrogel and 3D bioprinted structures. These results suggest that MXene nanocomposite bioinks and their 3D bioprinting with high electrical conductivity, biocompatibility and degradability can synergize some new applications for tissue and neural engineering.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscale Most Popular 2020 Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...