Precise design and synthesis of Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell nanofibers for the highly efficient catalytic combustion of toluene
Abstract
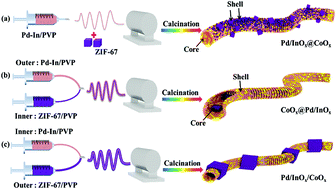
In this work, Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell nanofibers, CoOx@Pd/InOx core–shell nanofibers and Pd/InOx/CoOx nanofibers with different morphologies have been successfully synthesized for the catalytic combustion of toluene. Among them, the Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell sample is novel and composed of Pd/InOx nanotube cores, CoOx nanocubes and CoOx nanoparticle shells derived from ZIF-67. On the contrary, the CoOx@Pd/InOx core–shell catalyst is assembled by CoOx nanocube cores and Pd/InOx nanotube shells. Finally, the Pd/InOx/CoOx nanofibers as references are synthesized by a method similar to the synthesis of the CoOx@Pd/InOx core–shell sample. Interestingly, the Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell sample displayed the best activity for toluene oxidation with T90 = 253 °C, good thermal stability and good cyclic stability during three runs. Through some characterizations, it was verified that the Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell sample exhibited the best performance for toluene oxidation reactions due to a larger specific surface area, higher reducibility, more abundant structural defects and oxygen vacancies, higher proportion of Pd0 and Co3+ species and higher lattice oxygen species than others. Simultaneously, the Pd/InOx@CoOx core–shell sample exhibited good thermal stability and cyclic stability, which might be due to the layer of the CoOx shell to protect the stability of the Pd nanoparticle core.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...