Near-infrared control and real-time detection of osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells by multifunctional upconversion nanoparticles†
Abstract
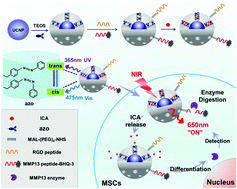
Finding a method to control and detect the differentiation of stem cells in real time remains a challenge for regenerative medicine. Here we developed the multifunctional upconversion nanoparticle (UCNP) approach for both near-infrared (NIR) control and the real-time detection of osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). We first synthesized Tm/Er doped core–shell UCNPs (NaYF4:Yb/Tm/Er@NaYF4), and the core–shell UCNPs were coated with mesoporous silica for drug loading and installing photomechanical azobenzene (azo). Then the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide and the matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) sensitive peptide-black hole quencher-3 group (CGPLGVRGK-BHQ-3) were conjugated on the surface of UCNPs for cell targeting and detection of cell differentiation. The final multifunctional UCNPs are called UCNP@mSiO2-azo-peptide-BHQ-3. The drug icariin (ICA), which can induce the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, was loaded into UCNP@mSiO2-azo-peptide-BHQ-3 to form the UCNP nanocomplexes. ICA could be released from UCNP nanocomplexes in a NIR-controlled manner that is based on the transformation of the trans-isomer of azo into the cis isomer under the upconverted UV and visible light. Meanwhile, UCNP@mSiO2-azo-peptide-BHQ-3 could also be used as a nanoprobe to detect the activity of the MMP13 enzyme by enzyme digestion and UCNP fluorescence recovery. By detecting MMP13, which is produced by osteogenic differentiation, a real-time detection of cell differentiation in living differentiated MSCs could be achieved using UCNP nanoprobes. Thus, the multifunctional UCNPs combined the control of cell differentiation with the real-time detection of cell differentiation in MSCs, which makes them a powerful tool for regulating and detecting the differentiation of MSCs in regenerative medicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...