Near-infrared -triggered release of tirofiban from nanocarriers for the inhibition of platelet integrin αIIbβ3 to decrease early-stage neointima formation †
Abstract
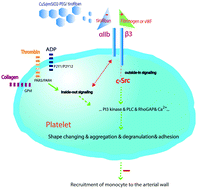
Platelets play an important role in the early stage of arterial remodeling after injury. Integrin GPIIb/IIIα (αIIbβ3) regulates platelet activation in the inside-out and outside-in signaling pathways. The use of tirofiban, an integrin αIIbβ3 inhibitor, in clinical therapy is limited by its short in vivo circulation time. Herein, a controlled drug-release system was formulated using CuS@mSiO2-PEG core–shell nanoparticles as near-infrared-triggered nanocarriers to release tirofiban on demand. The nanocarriers possessed good colloidal stability and very high loading efficiency for the integrin αIIbβ3 inhibitor (14.5 wt% for tirofiban). Local application of αIIbβ3 antagonist-tirofiban on an injured arterial wall inhibited platelet activation, which was accelerated by laser irradiation. Ex vivo platelet-promoted monocyte transmigration trans-well assays revealed decreased monocyte transmigration after platelet activation was inhibited by tirofiban. Two weeks after the wire-induced injury, the intimal area and cellular content were analyzed. The neointimal area was decreased in ApoE−/− mice with CuS@mSiO2-PEG/tirofiban and laser irradiation-promoted tirofiban release, which had limited the neointima formation. The lesions showed a decreased content of macrophages and smooth muscle cells compared with ApoE−/− mice without tirofiban inhibition. Therefore, the action of platelet-integrin αIIbβ3 in neointima formation after vascular injury was successfully inhibited in vivo through the controlled release of tirofiban using a near-infrared-triggered nanocarrier, leading to the decrease of early-stage neointima formation. This study also emphasizes the role of platelets in vascular remodeling and provides a new target, namely integrin αIIbβ3, for the inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia during vascular inflammation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...