A novel split mode TFBAR device for quantitative measurements of prostate specific antigen in a small sample of whole blood†
Abstract
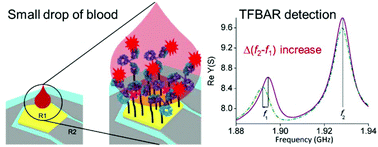
Easy monitoring of prostate specific antigen (PSA) directly from blood samples would present a significant improvement as compared to conventional diagnostic methods. In this work, a split mode thin film bulk acoustic resonator (TFBAR) device was employed for the first time for label-free measurements of PSA concentrations in the whole blood and without sample pre-treatment. The surface of the sensor was covalently modified with anti-PSA antibodies and demonstrated a very high sensitivity of 101 kHz mL ng−1 and low limit of detection (LOD) of 0.34 ng mL−1 in model spiked solutions. It has previously been widely believed that significant pre-processing of blood samples would be required for TFBAR biosensors. Importantly, this work demonstrates that this is not the case, and TFBAR technology provides a cost-effective means for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics and monitoring of PSA in hospitals and in doctors’ offices. Additionally, the accuracy of the developed biosensor, with respect to a commercial auto analyser (Beckman Coulter Access), was evaluated to analyse clinical samples, giving well-matched results between the two methods, thus showing a practical application in quantitative monitoring of PSA levels in the whole blood with very good signal recovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...