Facile synthesis of red dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescence sensing and cellular imaging†
Abstract
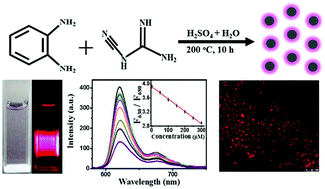
Recently, widespread attention has been paid to red emissive carbon dots (CDs) which have desirable optical properties, low toxicity, and biocompatibility. Despite great efforts, the facile preparation of red dual-emissive CDs useful for ratiometric detection and bioimaging remains challenging. Here, we report a facile synthesis of red dual-emissive CDs and their potential for ratiometric fluorescence sensing and cellular imaging. Derived from the hydrothermal treatment of dicyandiamide and o-phenylenediamine in dilute sulfuric acid, the CDs are surface-tailored with nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing functional groups. The as-prepared CDs show various good features, including good water solubility, biocompatibility, excitation-independent dual-emission with two photoluminescence (PL) peaks centered at 630 and 680 nm, and an absolute quantum yield (QY) of 30.2% in water. The CDs exhibit a selective, sensitive, rapid, and stable ratiometric fluorescence response toward methyl blue, giving a linear relationship in the range of 0.5–300 μM with a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.997. We also study ratiometric fluorescence sensing for the accurate detection of pH. Moreover, the CDs possess good cellular imaging ability, indicating their promising applicability for biomedical applications. These results pave a way toward the fabrication of red dual-emissive carbon-based nanomaterials useful for both ratiometric sensing and bioimaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...