Exquisite design of porous carbon microtubule-scaffolding hierarchical In2O3-ZnIn2S4 heterostructures toward efficient photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into CO†
Abstract
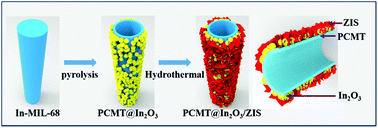
Porous carbon microtubule (PCMT)-scaffolding semiconductor heterostructures were exquisitely designed through the in situ growth of ZnIn2S4 (ZIS) ultrathin nanosheets onto In2O3 nanoparticle layers generated on the surface PCMT (abbreviated as PCMT@In2O3/ZIS) toward the efficient photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into CO. The pronounced photocatalytic performance for CO2 photoreduction into CO is attributed to a synergistic effect of the following factors: (1) the multistage hopping of the charge carriers among In2O3, ZIS, and PCMT greatly reduces the charge recombination in In2O3 and ZIS. (2) The mesoporous feature of the PCMT renders the large surface area and abundant active sites to accumulate the local concentration of CO2 in the heterostructures. (3) The existence of a large amount of carbon defects in PCMT promotes the activity of the absorbed CO2 molecules. (4) The tubular structures with two open ends of PCMT may favor the fast diffusion of the reactants and products, and the optical absorption can also be increased by multi-light scattering/reflection in the interior void. (5) The unique fabrication route leads to an intimate and tight contact among PCMT, In2O3, and ZIS, which is also favorable for the charge migration. This work makes a contribution to the development of a complex hollow photocatalysis system for artificial photosynthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...