Two-dimensional semiconducting Lu2CT2 (T = F, OH) MXene with low work function and high carrier mobility
Abstract
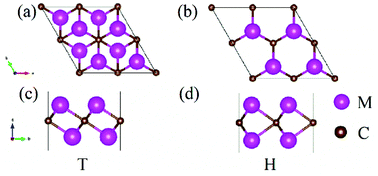
As a new family of two-dimensional materials, MXenes have attracted increasing attention in recent years due to their widespread potential applications. In contrast to early transition metals in convention, here we expand the M element of MXene to the rare earth element lutetium. Based on the first-principles density functional calculations, the bare lutetium-based carbide MXene Lu2C is determined to be stabilized in the T-type configuration. Furthermore, both fluorine and hydroxyl terminated configurations are found to be semiconductors, and their band gaps are suitable for use in semiconductors and visible and near-infrared optical devices. The Lu2C(OH)2 configuration shows a direct band gap and possesses an ultralow work function of 1.4 eV. Both Lu2CT2 (T = F, OH) MXenes exhibit high carrier mobilities. Particularly, the electron mobility of the Lu2C(OH)2 MXene is found to be anisotropic at room temperature, with values as high as 95.19 × 103 and 217.1 × 103 cm2 V−1·s−1 in the zigzag and armchair directions, respectively, which makes Lu2C(OH)2 a promising material for nanodevices. Based on these predicted properties, our work widens the range of MXene materials and their applications in semiconducting devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...