A nano-photosensitizer based on covalent organic framework nanosheets with high loading and therapeutic efficacy†
Abstract
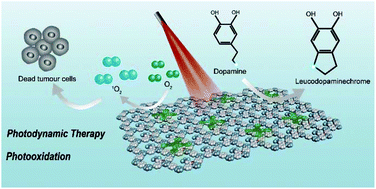
Photooxidation provides a promising strategy for photocatalysis, photodynamic therapy, and environmental protection. Unfortunately, most organic photosensitizers possess weak hydrophilicity and a π–π conjugated structure, leading to singlet oxygen self-quenching, poor loadability and therefore unsatisfactory photooxidation efficiency. Thus, dispersion of these photosensitizers within a two-dimensional porous covalent organic framework has become a feasible strategy to hinder their self-aggregation and augment their loading capacity. Here, we report a phthalocyanine-based photosensitizer loaded on covalent organic framework nanosheets. This nano-photosensitizer exhibits highly dispersed organic fluorescent phthalocyanines and a high loading capacity. The fabricated nanosheets restrict self-aggregation of photosensitizer molecules and enhance the photooxidation activity, which may offer a new paradigm for photooxidation and its multiple applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...