High resolution noncontact atomic force microscopy imaging with oxygen-terminated copper tips at 78 K†
Abstract
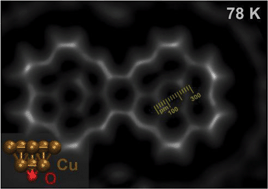
Functionalizing atomic force microscopy (AFM) tips by picking up single inert probe particles like CO or Xe from the surface drastically increase the resolution. In particular, this approach allows imaging organic molecules with submolecular resolution revealing their internal bonding structure. However, due to the weak coupling of these probe particles to both, the surface they are picked up from and the tip apex, these experiments require liquid helium temperatures (i.e. ≈5 K). In the present study we demonstrate that functionalizing an AFM tip with an atomically defined O-terminated copper tip (CuOx tip) allows performing such experiments at liquid nitrogen temperatures (i.e. ≈78 K) with outstanding quality. We show that it is possible to utilize CuOx tips for chemically selective imaging of a copper oxide nanodomain on a partially oxidized Cu(110) surface in the repulsive force regime at elevated temperatures. Moreover, the high structural and chemical stability of CuOx tips allow even ex situ investigations where these tips are used to perform experiments on other, non-Cu, non-oxidized, substrates. In particular, we present results obtained from a dicoronylene (DCLN) molecule with submolecular resolution. An analysis of inner and peripheral bond lengths of the DCLN molecule shows excellent agreement with theoretical gas phase simulations emphasizing the exceptional imaging properties of CuOx tips also at elevated temperatures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...