Trace fluorinated-carbon-nanotube-induced lithium dendrite elimination for high-performance lithium–oxygen cells†
Abstract
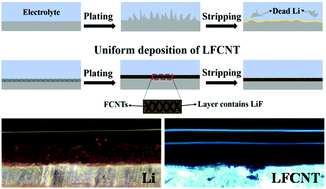
Lithium metal has attracted considerable attention due to its ultrahigh theoretical capacity. Nevertheless, issues such as dendritic Li formation and instability of the Li metal/electrolyte interface still restrain its practical applications. In this work, we design a Li composite anode with fluorinated carbon nanotubes (FCNT) fabricated by a simple melting–soaking method. It was found that trace amounts of added FCNT (only 1.6 wt%) lead to a significant chemical/electrochemical stability of metallic Li. The obtained Li/FCNT composite electrode (LFCNT) exhibits much better stability in open air and electrolyte than bare Li. The LFCNT enables uniform plating/stripping of metallic Li, preventing the dendrite formation during repeated cycling. In situ optical microscopy observations confirm dendrite-free Li deposition with the mechanism clarified by density functional theory calculations. Compared with bare Li, the LFCNT shows a considerable improvement in rate capability, voltage hysteresis and cycle performance, sustaining stable cycling at a high current density of 3 mA cm−2 or a capacity up to 5 mA h cm−2. Li–O2 cells with a LFCNT anode exhibit a long life of 135 cycles at a capacity of 1000 mA h g−1, which is six-fold than that with the bare Li anode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...