Fluorescence studies and photocatalytic application for hydrogen production of ZnII and CdII complexes with isophthaloylbis(thioureas)†
Abstract
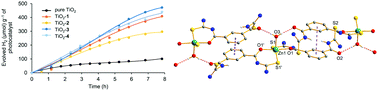
This work is related to ZnII and CdII complexes with isophthaloylbis(thioureas), describing the synthesis, characterization and fluorescence properties. In this work, the crystal structure of isophthaloylbis(N,N-diphenylthiourea) is described as a dimethyl sulfoxide solvated molecule. Complexes [Zn2(LEt)2] (1), [Cd2(LEt)2] (2), [Zn(HLPh)2(H2O)] (3) and [Cd2(LPh)2] (4) were characterized by infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry and elemental analysis. Complex 3 was also studied by NMR and Raman spectroscopies and by single crystal X-ray diffraction. It represents the first example of a complex with isophthaloylbis(thiourea) for further metal coordination, possibility given by the remaining O,S donor sets. Structural characterization was also performed for dimethyl sulfoxide adducts of complexes 1, 2 and 4, confirming the binuclear compositions through the O,S chelate coordination of both thioureate arms to the metal centers. Fluorescence studies were performed for the ligands and complexes 1–4 in which the width and intensity of the emission band of complexes 3 and 4 are greater than those presented by the ligands and complexes 1 and 2. TiO2-based composites were prepared with compounds 1–4, which have produced higher amounts of hydrogen than pure TiO2 by water splitting in experiments using a 300 W Hg/Xe lamp.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...