Anion binding with biphenyl-bis-urea derivatives: solution and solid-state studies†
Abstract
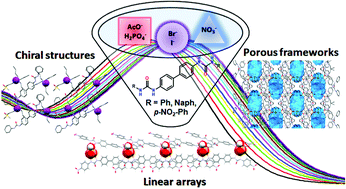
In this work, we have synthesized and characterized bis-urea derivatives 1–3, featuring a biphenyl spacer, and studied their anion binding properties in DMSO solution and in the solid state. In solution, 1 : 1 complexes were observed with association constant K values in the 103–104 M−1 range with a general preference for acetate over dihydrogenphosphate for all three receptors. We were also able to obtain and characterize, by X-ray diffraction on single crystals, ten receptor–anion complexes including acetate and dihydrogenphosphate, as well as monohydrogenphosphate, halides and the nitrate ion. Linear (anion–receptor)n arrays, porous frameworks and non-centrosymmetric structures were observed and described in detail.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...