Synthesis of recoverable thermosensitive Fe3O4 hybrid microgels with controllable catalytic activity†
Abstract
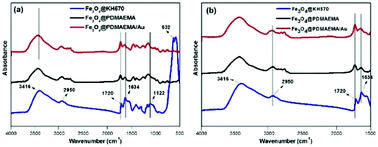
High-efficiency recoverable catalytic magnetite microgel particles, comprising a magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle (NP) core with a thermo-sensitive poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) polymer shell, were synthesized through a four-step procedure. The preparation route involved the following steps: (1) preparation of Fe3O4 NPs through a hydrothermal method; (2) attachment of double-bond functionalization to the surface of the NPs; (3) self-initiated photo-grafting and photopolymerization (SIPGP) of a monomer of 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA); (4) anchoring of Au onto Fe3O4@PDMAEMA magnetic microgel particles. Perfect surface functionalization was characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The Fe3O4@PDMAEMA–Au microgel particles exhibited excellent thermally adjustable catalytic activity for the typical reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). In addition, the Fe3O4@PDMAEMA–Au catalyst was responsive to an external magnetic field, allowing the microgel particles to be easily separated and recovered from water after the catalytic reaction. This type of novel smart microgel nanocatalyst has the potential to be applied as a high-performance, sustainable, catalytic system in the field of chemical synthesis, micromotors, and bio-molecule immobilization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...