Fabrication and characterization of polylactic acid/polycaprolactone composite macroporous micro-nanofiber scaffolds by phase separation
Abstract
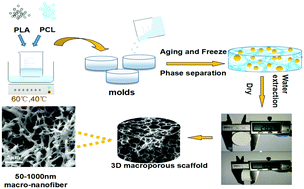
The realization of a three-dimensional (3D) composite nanofiber scaffold in bone tissue engineering is promising and challenging. In this paper, a series of biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA)/polycaprolactone (PCL) composite micro-nanofiber scaffolds with different PCL contents (0–50 wt%) were prepared by phase separation. The results showed that the addition of PCL had a great effect on the morphology of composite scaffolds and also changed the thermal properties and crystallinity of the PLA matrix. Meanwhile, the addition of the PCL content less than 30% could improve the compressive modulus of the PLA/PCL composite scaffold but slightly reduce the compressive strength. However, a higher content of PCL caused macroscopic collapse of the composite scaffold, which gradually deteriorated the mechanical properties of the scaffolds. The apatite formation ability, in vitro cell proliferation and degradation experiments showed that the PLA/PCL composite scaffold with 30% PCL has good bioactivity, cytocompatibility and degradation rate compared to the pure PLA scaffold just due to the biomimetic ECM nanofiber structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...