Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling studies of conophylline inspired novel indolyl oxoacetamides as potent pancreatic lipase inhibitors†
Abstract
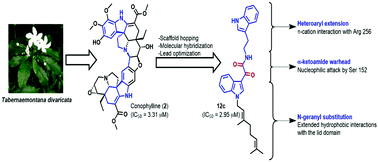
A novel series of 21 indolyl oxoacetamide analogues was designed based on the natural product lead conophylline, and evaluated for their pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity using porcine pancreatic lipase (Type II). Analogues 12c and 12b exhibited comparatively greater potential (IC50 values of 2.95 and 3.26 μM) than conophylline (IC50 – 3.31 μM), while the standard drug, orlistat, exhibited a potent IC50 value of 0.99 μM. Further, analogues 12b and 12c exhibited reversible competitive inhibition similar to orlistat and conophylline, and possessed Ki values of 1.89 and 1.69 μM, respectively. Molecular docking of these analogues was in agreement with the in vitro results, wherein the MolDock scores exhibited significant correlation with their inhibitory activity. A 10 ns molecular dynamics simulation of 12c complexed with pancreatic lipase confirmed the role of extended alkyl interactions, along with π–π stacking and π–cation interactions, in stabilising the ligand in the active site (maximum observed RMSD ≈ 3.5 Å). ADMET prediction indicated the GI absorption of these analogues to be high; however, they did not possess carcinogenicity and hepatotoxicity in contrast to orlistat and conophylline.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...