DFT studies on the reaction mechanism for the selective oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkanes by BN catalysts†
Abstract
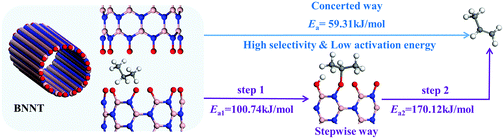
The oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) reaction mechanism of ethane and propane catalyzed by two kinds of oxygen-species-terminated BN materials, namely BN nanotubes and h-BN, was studied by the B3LYP-D3 functional with the 6-31G(d,p) basis set. On the atomic-oxygen-species-terminated active sites, two hydrogen atoms of the alkane were abstracted to form an alkene in a concerted way, which was more favourable than the stepwise mechanism from kinetic and thermodynamic viewpoints. The concerted way could lead to excellent selectivity to alkenes because without intermediate to side-product. The steric structural match between the alkane and oxygen species was thought to be the major effect factor to determine the ODH mechanism. Active oxygen species were recovered through the hydroxyl coupling into water with an activation energy (238.17 kJ mol−1) close to experimental data (253 kJ mol−1). By investigating the transformation kinetics from hydroxyl-terminated species to active-oxygen-terminated species, the active-site regeneration was speculated to be the rate-limiting step of ODH. Stepwise oxidative dehydrogenation happening in a rebound mechanism could explain the formation of COx side-product, although its activation energy was much larger than that for the concerted way. The propyl intermediate kinetically favourably proceeded through a second hydrogen abstraction to form propylene rather than C–C bond cleavage to form ethylene. These results would provide helpful information to precisely design oxygen-functionalized BN catalysts for ODH.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...