Oxygen-defective ZnO porous nanosheets modified by carbon dots to improve their visible-light photocatalytic activity and gain mechanistic insight†
Abstract
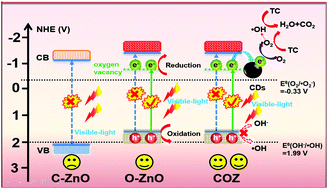
The introduction of defect engineering and the addition of a co-catalyst in the design process of semiconductor photocatalysts are both effective modified routes to improve the photocatalytic activity. In this work, a carbon dots/oxygen-defective ZnO (COZ) porous nanosheet composite photocatalyst was prepared via a one-step liquid-phase wet chemistry method for the highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline (TC). Moreover, an optimal photocatalytic performance was exhibited in the COZ-50 sample (nearly 86% degradation of TC within 21 min of irradiation). Benefitting from the expansion of specific surface area and light absorption as well as an effective separation of photo-induced charges due to the existence of oxygen defects and the introduction of CDs, the COZ composites presented outstanding photocatalytic and mineralization activity. The photocatalytic reaction mechanism on COZ was also revealed in detail through active species capture experiments and electron spin resonance (ESR) techniques. Ultimately, the possible photodegradation pathway of TC was proposed based on the detection of intermediates by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...