Biomass-derived Cu/porous carbon for the electrocatalytic synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and diols under mild conditions†
Abstract
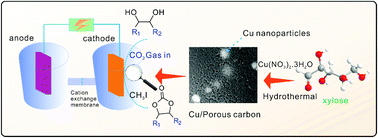
Biomass-derived Cu/porous carbon (Cu/PC) composites were facilely assembled by using a one-pot hydrothermal approach combined with calcination under a N2 atmosphere, and were used for the electrocatalytic synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and diols at room temperature and normal pressure without any other catalysts. The results show that the Cu/PC composites with large specific surface areas (SBET > 279 m2 g−1) and high pore volumes (Vp > 0.47 cm3 g−1) possess good catalytic activity for CO2 electrocatalytic fixation. The Cu nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed in the PC, resulting in a remarkable increase in the catalytic activity of the composite compared with those of pure PC and Cu sheets. In addition, the Cu content influenced the electrocatalytic activity. Among the materials used, Cu/PC-III was the best cathode as it had a 46.3% electrosynthesis yield of propylene carbonate, wide application prospects and was suitable for the synthesis of other o-diols. The yield of 4-propyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one reached 57.8%. The prepared composites also displayed satisfactory reusability, and the yield was not reduced even after six cycles of use. These results reveal that the composites could be effectively used for the electrosynthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and diols under mild conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...