Organic–inorganic bimetallic hybrid particles with controllable morphology for the catalytic degradation of organic dyes†
Abstract
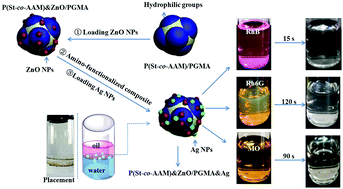
We report a successful fabrication of popcorn-shaped amphiphilic organic–inorganic bimetallic P(St-co-AAM) & ZnO/PGMA & Ag hybrid nanoparticles (NPs) for the efficient catalytic degradation of organic dyes. First, the controllable structures of anisotropic P(St-co-AAM)/PGMA NPs were synthesized via the emulsifier-free seeded emulsion copolymerization of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) based on the copolymerized seeds of styrene (St) and acetoacetoxyethyl methacrylate (AAM). The investigation results revealed that the formation of asymmetric composite particles was generally attributed to the thermodynamic immiscibility between PS and PGMA, and the introduction of hydrophilic AAM in the seeds advanced both phase separations. ZnO NPs were preferentially anchored on surface of the PAAM domains due to the interplay with β-diketone groups, while Ag NPs were successfully loaded on amino-functionalized PGMA domains due to the chemical bonding between silver ions and amino groups. When the P(St-co-AAM) & ZnO/PGMA & Ag hybrid particles were applied in the catalytic degradation of rhodamine B (RhB), rhodamine 6G (Rh6G), and methyl orange (MO), excellent catalytic activity could be obtained in which the three dyes were completely degraded within two minutes, showing the potential application in removing organic dyes from industrial waste water. The excellent activity of the catalyst was caused by its unique Janus structure, highly uniform distribution of metal NPs, and bimetallic synergic effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...