Facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ag–SnS nanocomposites†
Abstract
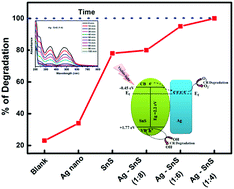
Tin sulfide (SnS), being a simple binary compound containing earth abundant, cheap and less toxic elements, has emerged as a potential material in photocatalysis and photovoltaics due to its unique optical and electrical properties. Furthermore, the properties of SnS can be enhanced by either doping or nanocomposite formation with suitable metals, but remains scantly explored. Here, we report the synthesis of Ag–SnS nanocomposites via a hot injection method from their respective Ag and SnS precursors and studied the photocatalytic activity of these nanocomposites. The formation of Ag–SnS nanocomposites with varying amounts of SnS and Ag is confirmed from PXRD, FESEM, and TEM studies, while the Ag(0) state in these nanocomposites is inferred from photoelectron spectroscopy studies. The Ag–SnS nanocomposites show better photocatalytic activity towards degradation of Congo red (CR) dye in the visible region as compared to the activity of pristine SnS and Ag samples. Furthermore, the photocatalytic efficiency enhanced by increasing the amount of Ag and 100% CR dye degradation is achieved in 100 minutes using the Ag–SnS nanocomposite with a molar ratio of 1 : 4. Higher photocurrent and reduced peak intensity in the PL study of the Ag–SnS (1 : 4) nanocomposite suggest more charge separation, which is largely responsible for the enhanced photocatalytic activity. The scavenger study suggests that the photo-generated superoxide radicals and holes are the primary-active species for the photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...