tert-Butyl-substituted bicarbazole as a bipolar host material for efficient green and yellow PhOLEDs†
Abstract
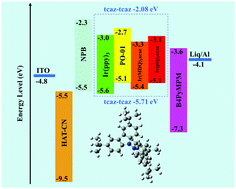
For host materials, a high triplet energy (ET) value and good charge transporting ability with appropriate frontier orbital energy are vital properties to achieve efficient phosphorescent organic light emitting diodes (PhOLEDs). A novel host material, 3,3′,6,6′-tetra-tert-butyl-9,9′-bicarbazole (tcaz–tcaz), was designed and synthesized by an intermolecular N–N coupling reaction of 9,9′-bicarbazoles. The compound displays excellent thermal and morphological stability with a decomposition temperature (Td) of 302 °C and a small value of root-mean-square (RMS) roughness less than 0.670 nm for neat film, respectively. In addition, tcaz–tcaz possesses a high ET value of 3.0 eV and suitable HOMO/LUMO of −5.71 eV/−2.08 eV. Tcaz–tcaz hosted devices exhibit maximum external quantum, power and current efficiencies of 15.5%, 40.0 lm W−1 and 56.1 cd A−1, respectively, with a low turn-on voltage of 2.4 V for Ir(ppy)3 and 11.0%, 35.6 lm W−1 and 35.9 cd A−1 for PO-01. Orange and red devices were also fabricated, showing inferior performance with a maximum external quantum efficiency of 3.81% for Ir(MDQ)2(acac) and 6.41% for Ir(piq)2(acac), respectively. Thus, tcaz–tcaz is promising for utilization as a host material for the future exploration in multi-colour PhOLEDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...