The highly efficient and selective dicarbonylation of acetylene catalysed by palladium nanosheets supported on activated carbon†
Abstract
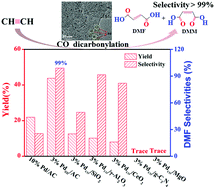
The carbonylation reaction is an atom economic and efficient approach for carbonyl group construction. The challenge of the conversion lies in the realization of high-selectivity and activity during the reaction. Herein, a PdCO/AC catalyst, with palladium (Pd) nanosheets loaded on activated carbon (AC) surface, was synthesized to evaluate the structure–activity relationship. As expected, the PdCO/AC catalyst has higher catalytic reactivity (43.8%) and selectivity (99.0%) when compared with commercial Pd/AC catalyst (conversion: 21.9%, selectivity: 25.5%). The thermodynamic effect of the Pd morphology was shown by the reduced activation energy (Ea ∼ 9.61 kJ mol−1) of the reaction. Based on catalytic evaluation results and catalyst characterization, the strong effect of the Pd nanosheet morphology on the reaction performance is mainly due to special electronic and compositional structures on the Pd(111) crystal plane, which might increase the activation capacity toward carbon monoxide. In addition, comparative experiments examining the support effect, initial total pressure, O2 concentration, and pH value were conducted to determine the optimal reaction conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...