Designing a new class of excess electron compounds with unique electronic structures and extremely large non-linear optical responses†
Abstract
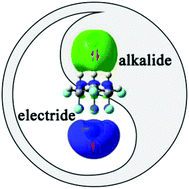
An intriguing class of excess electron compounds with unique electronic structures was obtained on the basis of a facially polarized molecule, namely, all-cis-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexafluorocyclohexane (1). By doping two different faces of this Janus molecule with an alkaline earth atom and an alkali-metal atom, a series of M-1-M′ (M = Be, Mg, and Ca; M′ = Li, Na, and K) compounds were first constructed. The calculated results show that unlike Be and Mg, one 4s electron of Ca in Ca+-1-M′− (M′ = Li, Na, and K) can be transferred to the upper alkali metal atom, thus forming an alkali metal anion, while the remaining 4s electron of Ca is pushed away from Ca+, yielding localized electrons around it by the instinctive facial polarization of 1 or with the assistance of oriented external electric fields (OEEFs). Interestingly, these novel compounds exhibit extremely large first hyperpolarizabilities (β0) in the range of 9.94 × 105–1.81 × 106 a.u. and high stability. Thus, this work can provide first members simultaneously containing typical alkalide features and electride-like characteristics to further enrich the family of excess electron compounds and offer novel candidates for NLO materials with high performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...