Construction and application of a nonenzymatic ascorbic acid sensor based on a NiO1.0/polyaniline3.0 hybrid
Abstract
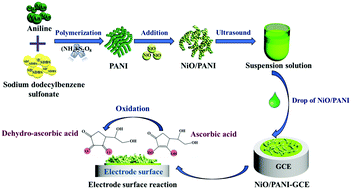
NiO1.0/PANI3.0 was prepared using an in situ polymerization one-pot method and applied in the detection of ascorbic acid (AA). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were used to optimize the modified electrodes with different composite materials. The linear relationship between peak oxidation current and the square root of scan rate indicates that the redox reaction on the NiO1.0/PANI3.0 modified electrode was controlled by concentration diffusion. The linear equation between peak current and AA concentration is I (μA) = 2.679 + 0.2093C (μM) and the correlation coefficient is 0.997. The sensitivity was 2990 μA mM−1 cm−2, and the limit of detection (LOD) was 12.85 μM. The results are comparable with other reported electrode materials. Moreover, the tests of EIS, CVs, DPV, and i–t curves revealed that the as-prepared NiO1.0/PANI3.0 modified electrode had low impedance, good reproducibility and repeatability, high stability, and strong anti-interference ability in AA detection. In addition, the constructed AA sensor successfully detected AA in real samples such as orange juice, lemon, and bread, and the percentage recovery varied from 97.95 to 104.93% (n = 5). Therefore, the low cost NiO1.0/PANI3.0 sensor with simple preparation has great prospects for development in food monitoring, health care and other industries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...