Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic zinc coatings with corrosion resistance via an electrodeposition process
Abstract
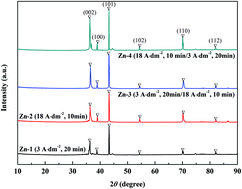
In this investigation, we demonstrated a controlled electrodeposition method by varying the current density to generate hierarchical structures of zinc (Zn) on a carbon steel surface, which serves as a hydrophobic and anticorrosion coating when further modified by stearic acid to form a covalently bonded layer that offers low surface energy. The chemical composition, surface morphology and roughness of the modified Zn coatings were analyzed via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The water contact angle and wettability tests have shown that the modified Zn coating with a micro/nanostructure displayed a water contact angle of 158.7° and a sliding angle of 6.4°, indicating strong superhydrophobicity. Interestingly, the modified Zn coating with a micro/nanostructure exhibited strong mechanical stability during knife scratching and adhesive tape peeling tests. In addition, the modified superhydrophobic Zn coating showed improved corrosion resistance that provided protection to the carbon steel. The protection mechanism can be attributed to the hierarchical micro/nanostructure of the Zn surface itself and the formation of a hydrophobic zinc stearate complex compound. The superhydrophobic Zn coating has good application prospects in a neutral corrosion environment, where it retards corrosion and reduces the adhesion of water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...