Simultaneous sensitive analysis of Cd(ii), Pb(ii) and As(iii) using a dual-channel anodic stripping voltammetry approach
Abstract
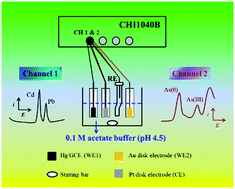
Cd, Pb, and As ions are common heavy metal ions that are highly toxic to the environment and human health. In order to develop a portable, fast and facile approach to analyze these heavy metal ions, especially in situ identification, a dual-channel anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV) approach was proposed to simultaneously analyze the trace Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(III). By using an Au electrode for dual-signal ASV analysis of As(III) and a Hg- or Bi-plated glassy carbon electrode for ASV analysis of Cd(II) and Pb(II) on a multichannel potentiostat, different heavy metal elements that are more active than Hg (negative-potential group: Cd and Pb) or more inactive than Hg (positive-potential group: As) can be detected in one experiment (both in a single electrolytic cell and in two independent electrolytic cells). The limits of detection (at S/N = 3) are 0.03 μg L−1 for Cd(II), 0.05 μg L−1 for Pb(II), and 0.15 μg L−1 for As(III) in a single electrolytic cell, and are 0.06 μg L−1 for Cd(II), 0.08 μg L−1 for Pb(II), and 0.05 μg L−1 for As(III) in two independent electrolytic cells. These values are all below the provisional guideline values given by the World Health Organization. This new method that was applied in the ASV analysis of Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(III) in real environmental water samples also achieved satisfactory results. What's more, the dual-channel ASV protocol may be extended to simultaneous ASV analysis of many other heavy metal ions (Hg, Cr, Cu, Zn, etc.).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...