Effects of Cu2+ incorporation on ZnAl-layered double hydroxide
Abstract
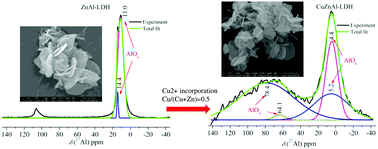
To investigate the structural properties of Cu2+-incorporated ZnAl-layered double hydroxide, a series of CuZnAl-layered double hydroxides with various 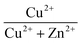 molar ratios was prepared by the constant pH co-precipitation method. The composition, structure and morphology of the synthesized products were analyzed by using XRD, SEM, TEM, FTIR, XPS and 27Al–1H MAS-NMR techniques. The results show that all samples with or without copper present crystalline LDH with a flower-like architecture, and no other impurity was observed. The interesting observation of the study was that the incorporation of copper influences the coordination number of aluminum. Comparing with the ZnAl-LDH layers, which contained only ZnO6 and AlO6 octahedra, in the Cu-containing LDH layers, in addition to CuO6, ZnO6, and AlO6 species, the AlO4 species is clearly observed. A simplified explanation for the formation of AlO4 species is associated with the Jahn–Teller effect of copper. These results suggest that there are structural defects (Al–O–Al connectivities) in the form of AlO4 species in the Cu-containing LDHs.
molar ratios was prepared by the constant pH co-precipitation method. The composition, structure and morphology of the synthesized products were analyzed by using XRD, SEM, TEM, FTIR, XPS and 27Al–1H MAS-NMR techniques. The results show that all samples with or without copper present crystalline LDH with a flower-like architecture, and no other impurity was observed. The interesting observation of the study was that the incorporation of copper influences the coordination number of aluminum. Comparing with the ZnAl-LDH layers, which contained only ZnO6 and AlO6 octahedra, in the Cu-containing LDH layers, in addition to CuO6, ZnO6, and AlO6 species, the AlO4 species is clearly observed. A simplified explanation for the formation of AlO4 species is associated with the Jahn–Teller effect of copper. These results suggest that there are structural defects (Al–O–Al connectivities) in the form of AlO4 species in the Cu-containing LDHs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...