A magnetic hierarchical zero-valent iron nanoflake-decorated graphene nanoplate composite for simultaneous adsorption and reductive degradation of rhodamine B†
Abstract
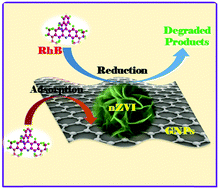
Zero-valent iron (ZVI) has been widely studied and utilized as a highly reductive agent for environmental remediation. In this study, a ZVI nanoflake-decorated graphene composite was successfully fabricated via the reduction of Fe2+ ions in ethanol solution. The new ZVI nanoflake-decorated graphene composite (GNPs@fZVI) (here GNPs are graphene nanoplates) was thoroughly characterized using scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy mapping, X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and magnetic measurements. The obtained GNP@fZVI composite consisted of hierarchical ZVI nanoflakes decorated on the surface of the GNPs. The hierarchical ZVI nanosheets presented a top layer of structural flake-like ZVI clusters with an average diameter of 1 μm and a bottom layer of uniform petal-like nanosheets with less than 10 nm thickness. The rhodamine B (RhB) removal performance of the resultant GNP@fZVI composite from aqueous solutions and the factors affecting the RhB removal efficiency of the composites were investigated. The results indicated that the as-prepared GNP@fZVI composite exhibited high RhB removal performance, and its removal efficiency was 100% after only 2.5 h of treatment using 3 g L−1 GNP@fZVI composite. Lastly, the probable simultaneous adsorption and reduction mechanism of the RhB dye using the GNP@fZVI composites was also discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...