New insights into two ciprofloxacin-intercalated arrangements for layered double hydroxide carrier materials†
Abstract
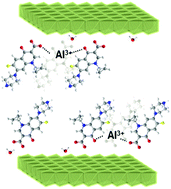
This paper describes the intercalation of ciprofloxacin (CIP), a bactericidal antibiotic, into the interlayer space of layered double hydroxides (LDHs). To counter the problem of bacterial resistance and also to improve the properties of the CIP drug, the drug carrier approach promises significant benefits. Through the tight control over the synthesis parameters, particularly the amounts of CIP with respect to aluminum ions, two different LDH-CIP-intercalated structures were obtained with significantly different interlayer distances, namely, 21 and 32 Å. The samples were fully characterized in terms of composition, structure, and morphology. Interestingly, the structure with the largest interlayer distance incorporated both CIP anions and Al(CIP)3 complex, exhibiting the possibility to increase the CIP drug loading beyond the anionic-exchange capacity of the LDH carrier. In vitro release in a simulated intestinal fluid (phosphate-buffered solution at pH 7.5) confirmed that LDH was a potentially efficient carrier to deliver CIP in a sustained manner via the anion-exchange mechanism. Different release rates were observed depending on the intercalated structure, which were also influenced by the morphological characteristics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Sustainability from intercalation compounds


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...