Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Bi2WO6 for the degradation of TC by synergistic effects between amorphous Ti and Ni as hole–electron cocatalysts
Abstract
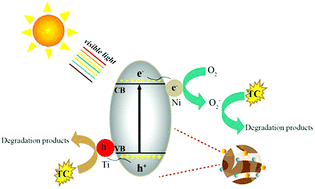
Novel Bi2WO6 nanoflakes co-modified by a Ni–Ti cocatalyst for the degradation of tetracycline (TC) were prepared via a hydrothermal and impregnation method. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), photoluminescence (PL) emission spectroscopy, and UV-vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy (DRS) techniques were used to explore the microstructures and optical characteristics of the photocatalysts. Also, the optimal Ni/Ti–Bi2WO6 composites with 2 wt% Ni and 5 wt% Ti achieved 93.5% removal efficiency of TC, which was higher than that of the pristine Bi2WO6 and Ti–Bi2WO6. Moreover, Ni/Ti–Bi2WO6 photocatalysts presented good stability after five degradation cycles. h+ and ˙O2− were the main active species, as revealed by the scavenger experiment. It revealed that the amorphous Ti and Ni as hole–electron cocatalysts can enhance the ability of the photocatalyst to absorb light and promote the transfer of photogenerated carriers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...