Effects of Au loading on the enhancement of photoelectrochemical activities of the Au@ZnO nano-heteroarchitecture
Abstract
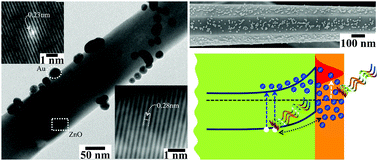
Heterostructures have delivered phenomenal photoelectrochemical performance owing to their excellent physicochemical properties. We report on the utilization of controlled Au@ZnO nano-heteroarchitectures for efficient water splitting. The ZnO nanowires of an average length and a diameter of ∼5–6 μm and 120 nm, respectively, synthesized by the hydrothermal method were subjected to the controlled decoration of Au nanoparticles of diameter ∼20 nm. The cubic crystalline Au nanoparticles were decorated on the hexagonal wurtzite ZnO nanowires under a controlled reaction time. A 12 h reaction time has resulted in the uniform decoration of Au nanoparticles along the surface of ZnO nanowires, and a further increase in the reaction time ensured their agglomeration in the array of ZnO nanowires. XPS analysis revealed the existence of pure metallic Au on ZnO nanowires without altering the stoichiometry. The Au@ZnO nano-heteroarchitecture with a 12 h reaction time delivered a maximum photocurrent density of 1.04 A cm−2, which is a 52-fold increase than that of pristine ZnO nanowires. The ABPE value is 0.59%, which is approximately five-fold higher than that of the pristine ZnO nanowires. This reveals that the controlled decoration of Au nanoparticles along the surface of ZnO nanowires has altered the Fermi energy position significantly and facilitated the injection of hot electrons from the SP state into the conduction band of ZnO, effectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...