Electrochemical studies on crystalline CuS as an electrode material for non-aqueous Na-ion capacitors†
Abstract
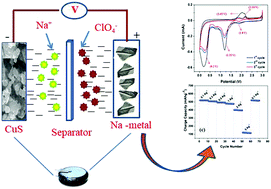
Current investigations are concentrated on the development of high-performance electrode materials for sodium-ion capacitors (NICs). Copper sulphide can be employed as an electrode material for sodium-ion capacitors owing to its electrical conductivity and specific capacity. Crystalline CuS provides a large surface area for Na insertion/extraction. In this context, we have reported CuS powder synthesised via a simple wet chemical route. XRD and FT-IR studies have been carried out to determine the phase formation and confirm the purity of the CuS powder. A specific surface area of 62 m2 g−1 is measured by a BET surface area analyser. NICs were assembled in a non-aqueous medium with CuS particles and investigated for charge–discharge cycling in the potential window from 0.01 to 3 V. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) confirmed that at a high scan rate from 10 mV s−1 to 100 mV s−1, the CuS particles showed ideal capacitive behaviour. The calculated value of specific capacitance was 160 F g−1 for the CuS particles. At a scan rate of 1 mV s−1, 74.8% capacitive contribution was obtained from the CuS particles. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) revealed the interfacial interactions of the CuS particles with an Na-based electrolyte.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...