Photoelectrochemistry of manganese oxide/mixed phase titanium oxide heterojunction†
Abstract
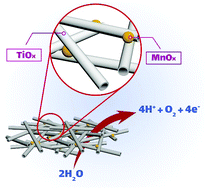
The aim of this study is to investigate the photoelectrochemical performance and behavior of mixed-phase titanium oxide, which was prepared through a high voltage method, and a manganese oxide heterojunction (Ti–TiOx–MnOx). In addition, the obtained results for Ti–TiOx–MnOx have been compared to the photoelectrochemical performance and behavior of titanium oxide nanotubes with a rutile phase, which is widely accepted as a reference due to the well-known photoelectrochemical performance, and manganese oxide heterojunction (Ti-nanotube–MnOx). The photoelectrochemical experiments showed that the application of stabilization potential and the presence and absence of dissolved oxygen significantly affected the photoelectrochemical properties of the Ti–TiOx–MnOx electrode. Exposing the Ti–TiOx–MnOx electrode to a stabilization potential of 1200 mV in the presence or absence of dissolved oxygen altered its oxidative photoelectrochemical response to a reductive photoelectrochemical response. However, the Ti-nanotube–MnOx electrode was not sensitive to the aforementioned conditions and always exhibited the same oxidative photoelectrochemical response. Scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy were exploited to characterize the prepared electrodes. These experiments showed that the deposited manganese oxide layer on both electrodes has a layered structure without long-range order. However, only the manganese oxide on the surface of the mixed-phase titanium oxide exhibited the expected photoelectrochemical response according to previous studies conducted on manganese oxide. Furthermore, according to the characterization experiments, it can be concluded that the different chemical environments of mixed-phase titanium oxide, containing both anatase and rutile phases, with oxygen vacancy sites may be one discernible reason for the observed different photoelectrochemical response of manganese oxide compared to titanium oxide nanotubes with a rutile phase.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...