Promotional effects of ascorbic acid on the low-temperature catalytic activity of selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia over Pt/SA: effect of Pt0 content†
Abstract
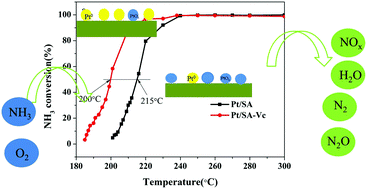
Low-temperature selective catalytic oxidation (SCO) is one of the important strategies used to remove the NH3 slip upstream of NH3 selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR). We have systematically studied the influence of the dispersity of active species, particle size and Pt0 content on the catalytic activity of ammonia oxidation with a Pt-based catalyst. Ascorbic acid was added to the modified Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 catalyst by the co-impregnation method for selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia (NH3-SCO), to explore the influence of different properties of the active components on the catalytic activity. It was found that addition of ascorbic acid changed the Pt0 content in the catalyst. Further studies found that increase in the Pt0 content could effectively promote activation of oxygen and facilitate more rapid conversion of O2 molecules to oxygen atoms. Thus, the dehydrogenation reaction of ammonia and oxygen atoms was promoted and proceeded at a lower temperature, improving the low-temperature activity of the NH3-SCO reaction. At the same time, it was shown that the Pt0 content in the system was the key factor affecting the NH3-SCO reaction, and this was confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, H2 temperature-programmed reduction and in situ diffuse-reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...