A procalcitonin photoelectrochemical immunosensor: NCQDs and Sb2S3 co-sensitized hydrangea-shaped WO3 as a matrix through a layer-by-layer assembly†
Abstract
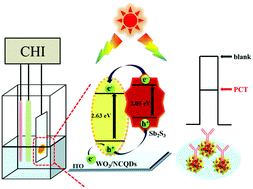
Using nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (NCQDs) and antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) to co-sensitize hydrangea-shaped tungsten trioxide (WO3), a novel photoelectrochemical (PEC) immunosensor was constructed to sensitively detect procalcitonin (PCT). WO3 possessed a three-dimensional structure with uniform size and large surface area on the indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode. NCQDs with abundant carboxy groups and excitation-independent PEC behavior were modified on the surface of the WO3 coating to enhance photochemical activity. Hence, the hydrangea-shaped WO3/NCQDs/Sb2S3 composite was obtained by modifying NCQDs and well-crystallized Sb2S3 nanoparticles on WO3 through a layer-by-layer assembly. It is worth noting that the photoelectric signal of WO3/NCQDs/Sb2S3 was about 8 times that of pure WO3 under visible light excitation. Moreover, the PEC immunosensor showed a large-scale response (0.001–100 ng mL−1) and a low detection limit (0.42 pg mL−1) under the best experimental conditions. This PEC immunosensor has advantages such as simplicity, facile fabrication, high sensitivity and strong stability, which have good research value in the analysis and detection of disease biomarkers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...