Staphylococcus aureus strains exposed to copper indium sulfide quantum dots exhibit increased tolerance to penicillin G, tetracycline and ciprofloxacin
Abstract
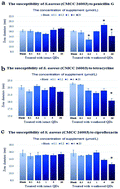
Copper indium sulfide, CuInS2 (CIS), semiconductor nanocrystals have the qualities of low toxicity, high absorption coefficient and near-infrared luminescence, and thus have attracted increasing attention due to their wide prospective applications in various fields. However, little is known about their potential biological effects, including their underlying toxicity on environmental bacteria and microcosms in water, especially pathogenic bacteria. In this work, two types of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus strains (S. aureus, CMCC 26003 and ATCC 25923) were used to investigate their antibiotic resistance changes to 14 types of antibiotics after exposure to intact CIS quantum dots and their weathered products. It was found that after exposure to certain concentrations of weathered CIS nanocrystals, S. aureus (CMCC 26003) exhibited increased tolerance to penicillin G, tetracycline and ciprofloxacin, whereas that of S. aureus (ATCC 25923) remained relatively unchanged. Moreover, the CIS quantum dot-exposed S. aureus (CMCC 26003) returned to their previous antimicrobial susceptibility level in the following generation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...