A cellulose substance derived nanofibrous CoS–nanoparticle/carbon composite as a high-performance anodic material for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
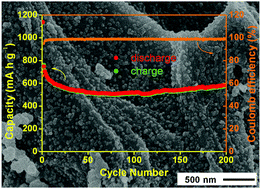
A hierarchical CoS–nanoparticle/carbon nanofibrous composite composed of CoS nanoparticles conformably anchored on the carbon fibres was fabricated by using a natural cellulose substance (e.g., ordinary laboratory filter paper) as the scaffold as well as the carbon source, and was applied as a high-performance anodic material for lithium-ion batteries. The initial cellulose substance (filter paper) was first carbonized at 450 °C, and then treated by KOH at 800 °C to acquire the activated carbon fibres; thereafter, the CoS nanoparticles were deposited onto the activated carbon fibres through a hydrothermal process. Such a porous three-dimensional network structure of the resultant CoS/carbon nanofibrous material inherited from the original cellulose substance resulted in high lithium ion diffusion coefficient, fast electronic transport and fine pseudo-capacitive effect. The composite with 37.0 wt% of cobalt sulfide displayed a high initial specific capacity of 1137.3 mA h g−1 and a stable reversible capacity of 576.7 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles at a current density of 100 mA g−1. Owing to the high specific surface area and porous structure of the CoS–nanoparticle/carbon nanofibrous composite, it delivered superior electrochemical performance during the lithiation/delithiation progress when used as an anodic material for lithium-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...