Polyaromatic hydrocarbon derivatized azo-oximes of cobalt(iii) for the ligand-redox controlled electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
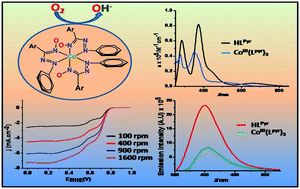
A pair of ligands HLPyr1a and HLAnc1b (Pyr = pyrene, Anc = anthracene) incorporating π-electron-rich polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), viz. pyrene and anthracene moieties respectively, in conjunction with electron-poor azo-oxime groups was synthesized. The tris complexes [CoIII(LPyr)3] 2a and [CoIII(LAnc)3] 2b were also prepared and structurally authenticated by X-ray diffraction. They exhibit significant redox and optoelectronic properties, which were analyzed by density functional theory (DFT) and time dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT). Theoretical investigation further revealed that the coordinated ligands act as superior electron reservoirs in comparison to the free ligands and transfer electrons through the PAH moieties. This property was smartly exploited to scrutinize the aptitude of the cobalt(III) complexes for the electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The catalytic process proceeds via a 4-electron transfer pathway to form hydroxide ions in alkaline medium. The role of the PAHs in the complexes 2a and 2b in providing a pool of electrons was further emphasized via substituting them with phenyl groups, as in [CoIII(LPh)3] 2c, when the catalytic ORR activity was significantly diminished. Moreover, the activity was completely lost when the PAHs were replaced by methyl groups, as in [CoIII(LMe)3] 2d.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...