g-C3N4/Uio-66-NH2 nanocomposites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution and oxidation of amines to imines†
Abstract
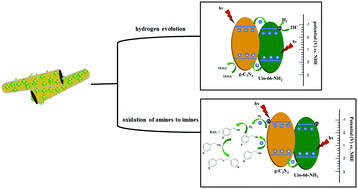
g-C3N4/Uio-66-NH2 (CNUIO) nanocomposites were prepared by growing an NH2-mediated zirconium-based metal–organic framework (Uio-66-NH2) in the presence of g-C3N4 nanotubes. CNUIO exhibited efficient photocatalytic performance in the oxidation of amines to imines and hydrogen production under visible light illumination. The optimal Uio-66-NH2 content in CNUIO was 16.7 wt% with a H2-generation rate of 152.2 μmol h−1, which is about 1.7 and 39 times as high as those of g-C3N4 and Uio-66-NH2, respectively. The optimal conversion rate of benzylamine was 58.9%, which is about 3.4 and 10.5 times as high as those of g-C3N4 and Uio-66-NH2, respectively. The probable photocatalytic mechanism of the CNUIO composite was investigated. This work provides a new insight into the fact that g-C3N4/MOF photocatalysts have great potential application in hydrogen production and organic synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...