Synthesis and characterization of an immobilized thiosalicylic–mercaptoethanol biligand system and its application in the detoxification of chromium(iii) and iron(iii) ions from tannery wastewater†
Abstract
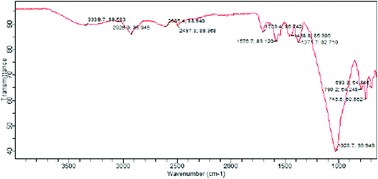
Effective wastewater treatments are of great importance to contemporary scientists, because the existing methods are ineffective for detoxifying tannery wastewater. This study aims to synthesize and characterize the polysiloxane-immobilized thiosalicylic–mercaptoethanol biligand system (PITSMCBLS) and use it in the detoxification of Cr3+ and Fe3+ in tannery wastewater. Porous, solid PITSMCBLS was prepared by hydrolytic polycondensation of tetraethylorthosilicate with a mixture of 3-chloropropyltrimethoxysilane, methanol and sodium hydroxide as a catalyst. The gelation formed (3-CPP) after 40 min, was functionalized (F-3CPP) with excess ethylchloroacetate and triethylamine, and grafted with a thiosalicylic–mercaptoethanol biligand. The PITSMCBLS was characterized using FTIR and SEM-EDX. The competitive sorption characteristics of the metal ions (Cr3+ and Fe3+) were studied using microwave plasma atomic-emission spectrophotometry (MP-AES). The FTIR spectrum of PITSMCBLS showed vibrational frequencies (cm−1) at: 3339, (O–H); 2928, (C–H); 2685, (SH); 2497, (Si–H); 1587–1707, (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and 1028, (Si–O). The SEM-EDX results showed irregular particle sizes (4.4294 ± 1.7187 nm) and an elemental composition (wt%) for 3-CPP of Si (50.45), O (25.02) and Cl (24.57). The F-3CPP showed an elemental composition (wt%) of O (58.68) and Si (41.32), whereas PITSMCBLS showed 11.94 of S. The Gibbs free energy yielded negative values for ΔG° (Cr3+ −14.187 to −14.832 and Fe3+ −14.369 to −14.843 kJ mol−1), and positive values for ΔH° (Cr3+ 5.345 and Fe3+ 0.000 kJ mol−1) and ΔS° (Cr3+ 64.459 and Fe3+ 47.421 J mol−1 K−1), respectively. Use of PITSMCBLS exhibits high potential for the extraction of Cr3+ and Fe3+ from tannery wastewater. The thermodynamic values indicated spontaneous, endothermic reactions and a high degree of disorderliness with respect to the metal ion binding capacity to the ligand system. This development would improve tannery wastewater treatment.
O) and 1028, (Si–O). The SEM-EDX results showed irregular particle sizes (4.4294 ± 1.7187 nm) and an elemental composition (wt%) for 3-CPP of Si (50.45), O (25.02) and Cl (24.57). The F-3CPP showed an elemental composition (wt%) of O (58.68) and Si (41.32), whereas PITSMCBLS showed 11.94 of S. The Gibbs free energy yielded negative values for ΔG° (Cr3+ −14.187 to −14.832 and Fe3+ −14.369 to −14.843 kJ mol−1), and positive values for ΔH° (Cr3+ 5.345 and Fe3+ 0.000 kJ mol−1) and ΔS° (Cr3+ 64.459 and Fe3+ 47.421 J mol−1 K−1), respectively. Use of PITSMCBLS exhibits high potential for the extraction of Cr3+ and Fe3+ from tannery wastewater. The thermodynamic values indicated spontaneous, endothermic reactions and a high degree of disorderliness with respect to the metal ion binding capacity to the ligand system. This development would improve tannery wastewater treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...