DFT investigation on the mechanisms of Csp3–H functionalization of glycine derivatives induced by radical cation salt†
Abstract
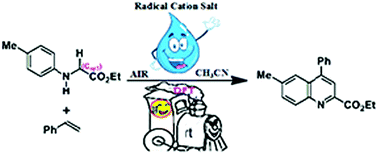
The mechanisms for the reaction between ethyl 2-(p-tolylamino)acetate and phenylethylene have been investigated at the M06-L-D3/6-311+G(d,p) level, and the SMD model was applied to simulate the solvent. The computational results suggest that the Csp3–H functionalization of ethyl 2-(p-tolylamino)acetate has two possible paths; then there are three probable paths (I, II or III) to yield the final product. In path I, one D–A addition reaction could produce the product compound; finally, the oxidative dehydrogenation could yield the product with the assistance of O2. The additive InCl3 can accelerate the D–A reaction via four possible paths, and the NOFF, FMOT and Fukui function can be applied to analyze the D–A reaction, while in paths II and III, the formed radical intermediate would go through a series of addition reaction, oxidation reaction, ring-closure reaction and oxidative dehydrogenation to yield the final product. The results could provide valuable insights into these types of interactions and related ones.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...