Enhanced flux of chemically induced hot electrons on a Pt nanowire/Si nanodiode during decomposition of hydrogen peroxide†
Abstract
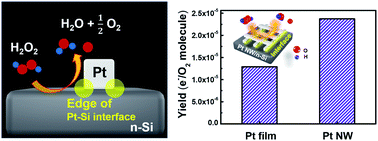
Identifying the charge transfer at metal–semiconductor interfaces by detecting hot electrons is crucial for understanding the mechanism of catalytic reactions and the development of an engineered catalyst structure. Over the last two decades, the development of catalytic nanodiodes has enabled us to directly measure chemically induced hot electron flux and relate it to catalytic activity. A crucial question is the role of interfacial sites at metal–oxide interfaces in determining catalytic activity and hot electron flux. To address this issue, a new design of catalytic nanodiodes employs nanoscale Pt wires and a semiconducting substrate. Here, we fabricated a novel Schottky nanodiode, a platinum nanowire (Pt NW) deposited Si catalytic nanodiode (Pt NW/Si) that exhibits an increased number of metal–semiconductor interfacial sites (Pt/Si) compared with a Pt film-based Si nanodiode (Pt film/Si). Two types of Pt/Si catalytic nanodiodes were utilized to investigate the electronic properties of the Pt/Si interface by detecting hot electrons and observing reactivity during the H2O2 decomposition reaction in the liquid–solid system. We show that the Pt NWs had higher catalytic activity because of the surface defect sites on the Pt NW surface. We observed a higher chemicurrent yield on the Pt NW/Si nanodiode compared with the Pt film/Si nanodiode, which is associated with the shortened travel length for the hot electrons at the edge of the Pt nanowires and results in a higher transmission probability for hot electron transport through metal–oxide interfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...