Ammonium phosphomolybdate: a material for dielectric crossover and resistive switching performance†
Abstract
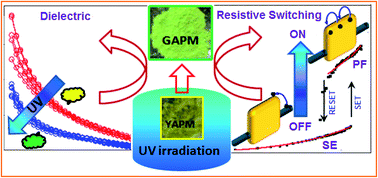
The yellow ammonium phosphomolybdate [(NH4)3PMo12O40] (YAPM) is a robust and elegant compound that has found innumerable field applications. Herein, we have shown that this inorganic polymer serves as a novel dielectric material and a compound for memory device fabrication. It displays changeable dielectric performance and ac conductivity under UV (∼365 nm) irradiation. Drastic lowering of the dielectric constant (ε′) was observed with the increase in dielectric loss factor, which was ascertained due to electron accumulation under UV exposure producing green APM (GAPM). The contributions of the Maxwell–Wagner polarization and the dipolar relaxation are correlated with the charge transfer and dielectric contribution of the material. Interestingly, the pressure-induced reduction of Mo(VI) to Mo(V) is reported for the first time and is similar to UV-exposed mixed-valence GAPM, which was corroborated by EPR spectra. In the ac signal, the crossover from quantum mechanical tunneling to hopping conduction is an adequate explanation for YAPM under UV irradiation. The fabricated device Au‖YAPM‖Au on a flexible paper substrate shows a resistive memory behavior that is modeled as a Schottky-type emission (SE) and Poole–Frenkel (PF) carrier transport for the OFF and ON states, respectively. The device exhibited a constant ON–OFF current ratio of 2 × 102 for YAPM. The OFF state endurance of the device (with 3 V pulses having 1 s time-period) under UV showed a steady increment current strength with time. After 100 s of UV exposure, the Au‖YAPM‖Au device became Au‖GAPM‖Au, and the conductivity completely shifted to a stable ON-state (at 300 s).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...