Long-term effects of impurities on the particle size and optical emission of carbon dots†
Abstract
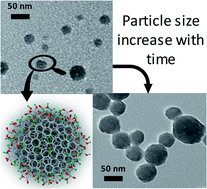
Carbon dots (CDs) are fluorescent nanoparticles that exhibit strong photoluminescence (PL) emission throughout the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Recent studies highlight the presence of fluorescent impurities in CD dispersions. Here, the long-term impact of these impurities on the stability of the physical and optical properties of CDs synthesized by the solvothermal method is studied. A significant increase in particle size is observed as a function of time after synthesis from transmission electron microscopy analysis of CDs. Furthermore, the quantum yield of blue PL emission, which is mostly caused by impurities that contain carboxyl groups, gradually decays from 30% to ∼3% over 13 weeks. The reduction in quantum yield is attributed to decomposition of impurities that, consequently, deposit on the particles and increase particle size. Finally, it is observed that the blue emission decreases considerably when CDs are properly purified and a solvent-dependent yellow emission arises. The yellow emission is almost negligible when CDs are dispersed in water; however, the intensity of yellow emission increases significantly when the concentration of ethanol is increased.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...